Day 1 :
Keynote Forum
Francis Eko
Morehouse School of Medicine, USA
Keynote: The VCG platform facilitates mucosal and systemic vaccine delivery for induction of protective immunity in the female genital tract
Time : 09:30-10:10

Biography:
Francis Eko is a Professor of Microbiology and Immunology at Morehouse School of Medicine, Atlanta (USA). His expertise is in “The development of vaccines and vaccine adjuvants”. His current research involves development of self-adjuvanting vaccines against chlamydia genital and respiratory infections and the effect of VCG-based adjuvants on immune responses to mucosal and systemic vaccines.
Abstract:
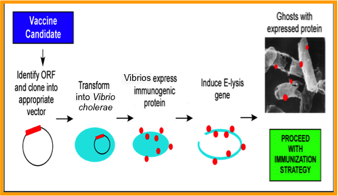
Statement of the Problem: The delivery vehicle and route of vaccine administration play an important role in the induction of optimal immune effectors and their homing to the site of infection to achieve protective immunity. The choice of an adequate route of vaccine administration is desirable to avoid compromising a potentially efficacious vaccine. We have designed a versatile Vibrio cholerae ghost (VCG) platform, an effective self-adjuvanting delivery vehicle capable of simultaneously delivering multiple vaccine antigens from the same or different pathogens to the immune system. It offers an attractive approach for developing vaccines against a number of human pathogens. The present study was undertaken to compare the potential of rectal mucosal and intramuscular systemic immunizations for induction of female genital tract immunity in mice using a VCG-based chlamydial vaccine.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: Groups of mice were immunized rectally (IR) or intramuscularly (IM) with VCG expressing the Chlamydia trachomatis porin B and polymorphic membrane protein D proteins (rVCG-PmpD/PorB; PmpD-vac) or glycoprotein D from HSV-2 (rVCG-gD2 or gD2) as antigen control. Vaccine efficacy was assessed by evaluating the intensity and duration of genital chlamydial shedding following intra-vaginal challenge with live chlamydiae. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare differences between groups.
Results: We demonstrated that both IM and IR immunization of mice with PmpD-vac elicited high levels of antigen-specific Th1 cell-mediated and humoral immune responses in mucosal and systemic tissues. Also, immunization reduced the length and intensity of genital chlamydial shedding following intra-vaginal challenge with live chlamydiae, irrespective of route of vaccine administration.
Conclusion & Significance: These results highlight the potential of the VCG platform for eliciting immunity in the female genital tract via both mucosal and systemic delivery of antigens in the absence of external adjuvants.
Keynote Forum
Giulio Tarro
Foundation de Beaumont Bonelli for Cancer Research, Italy
Keynote: From human vaccines for viral diseases to those ones for oncogenic viruses and tumor antigens
Time : 10:10-10:50

Biography:
Giulio Tarro completed his Graduation at Naples University (1962). He was a Research Associate in Division of Virology and Cancer Research at Children’s Hospital (1965-1968); Assistant Professor of Research Pediatrics, College Medicine (1968-1969) at Cincinnati University, Ohio and; Professor of Oncological Virology at Naples University (1972-1985). He was a Chief in Virology division (1973-2003), Head in Department of Diagnostic Laboratories (2003-2006) at D. Cotugno Hospital for Infectious Diseases, Naples. Since 2007, he has been Chairman of Committee of Biotechnologies and Virus Sphere at World Academy Biomedical Technologies, UNESCO and; Adjunct Professor in Department of Biology at Temple University. His researches have been concerned with the characterization of specific virus-induced tumor antigens, which were the finger-prints left behind in human cancer.
Abstract:
The Variola major, the virus that causes the smallpox, lethal virus in the 30% of the cases, was eradicated in 1979 in the human species, thanks to a capillary vaccination on global scale. Recently, the World Health Organization declared that India and Southeast Asia are polio free; really a great achievement since the vaccine for polio, an infectious disease that can cause paralysis, was certificated safe and useful only 60 years ago. Last year over 800 million doses of combination vaccines are going to be used to vaccinate Chinese children whereas more than 20 million children worldwide do not receive one or more important vaccinations that would protect them from at least one preventable disease. Research is badly needed to develop strategies to communicate the importance of vaccinations to uncertain parents. The 2008 San Diego measles outbreak costed over 10.000 dollars for each infection in comparisons to the total cost to contain the outbreak (approximately 124.000 dollars). Even if there are rare cases of vaccine damage, the research to facilitate vaccination must be done to prevent diseases. The vaccine for HBV virus, responsible for hepatitis B infection is able to prevent 50% of all liver cancers. Human papilloma viruses (HPV) have been correlated with the cervical cancer (genotypes 16 and 18 particularly oncogenic in humans): the USA Food and Drug Administration in 2006 released the first vaccine against HPV. Long years of research were required for busting the new system to fight cancer. Research is going to obtain the complete sequence by proteomics approaches, in order to achieve adequate antigen preparations that might be used to generate assays for a specific anticancer vaccine. Finally, the ability of the immune system to recognize a tumor-associated antigen, thus enabling development of a vaccine approach for therapeutic application, represents a main target of this field of research.
