Aleksandra Inic-Kanada
Center of Ocular Inflammation and Infection, Austria
Title: Use of corpuscular adjuvants for ocular mucosal immunization as a strategy for vaccine against trachoma
Biography
Biography: Aleksandra Inic-Kanada
Abstract
Statement of the Problem: Trachoma is the world's most common cause of preventable blindness from infectious origin and is prevalent in most rural areas throughout the developing world. It has been classified as one of the five most neglected tropical diseases.
Aim: Our overall goal is to develop an innovative, prophylactic, needle-free, safe and effective mucosal vaccine against Chlamydia trachomatis (Ct) that will prevent or reduce clinical trachoma thereby reducing chlamydia induced morbidity. The strategy employed is to reproduce and improve naturally acquired protective immunity by using a mucosal immunization strategy: eye drops mimicking the natural infection route.
Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: Immuno-proteomic profiling of sera of subjects from trachoma endemic regions enabled us to confirm the chlamydial adhesins (major outer membrane protein and polymorphic membrane proteins) as vaccine candidates. In combination with these antigens, different corpuscular adjuvants were used and tested in animal models.
Results: We have proved that eye drop vaccination irrespective of the adjuvant applied elicits higher immune response at the site of infection by blocking Ct-host cell entry with enhanced immune responses against key adhesins involved in infection.
Conclusion & Significance: The combination of relevant chlamydial adhesins and an effective adjuvant could represent a vaccine approach to achieve a protective immunity. Ocular mucosal immunization strategy might lead to a needle-free ocular mucosal vaccine suitable to overcome the current hurdles in managing trachoma and will thus have a major global impact.
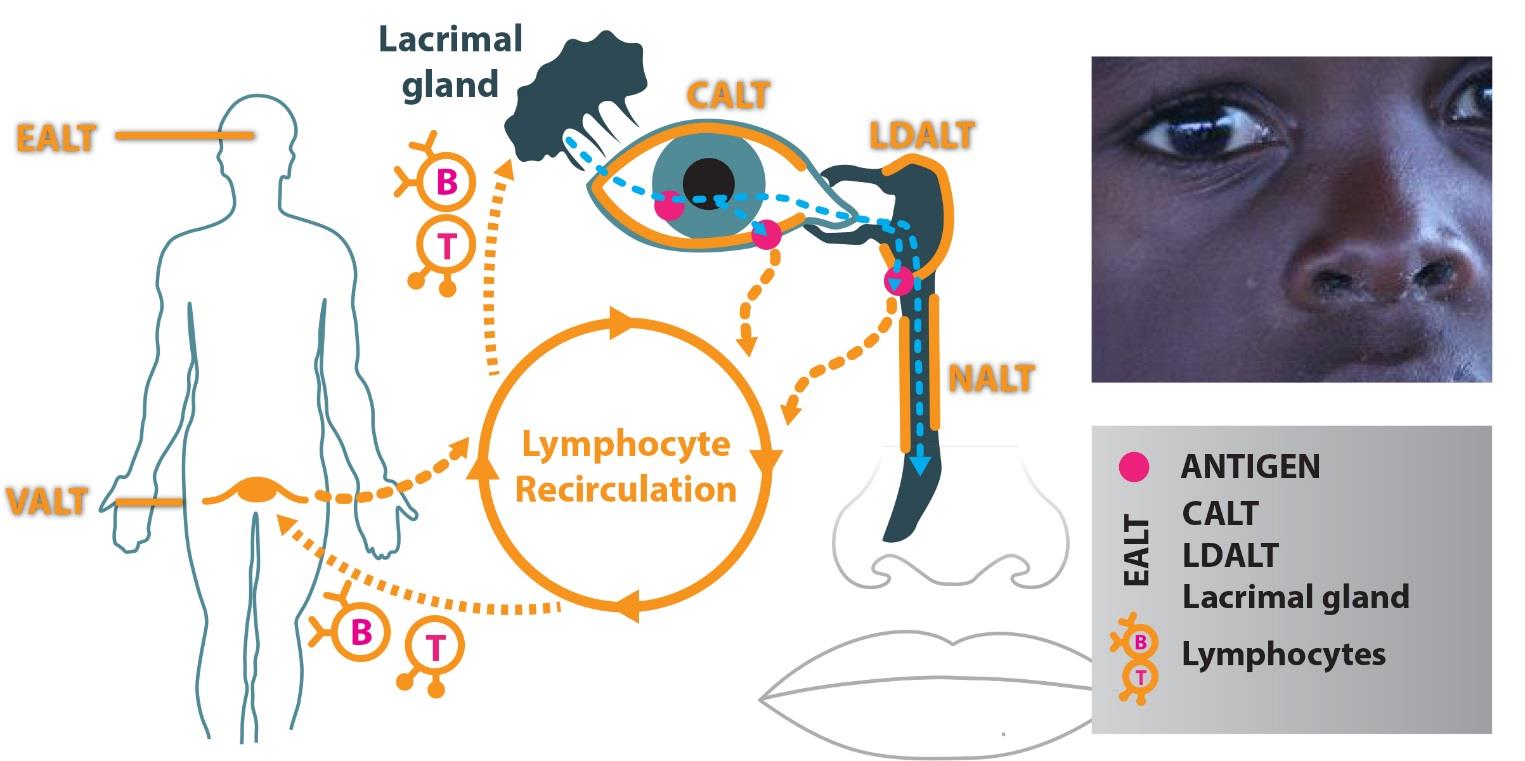
Figure 1: The eye-associated lymphoid tissue (EALT) includes the lacrimal gland, conjunctival-ALT (CALT) and lacrimal drainage-ALT (LDALT). It is a part of the immune system, which is essential to protect the organism from ocular infection with a specific IgA based immune response.





